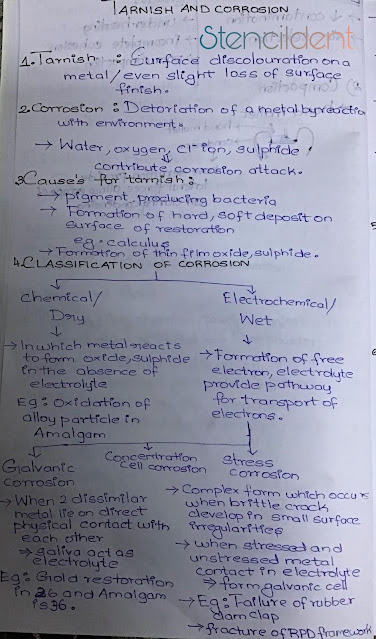
Function of saliva ,salivary component and its probable mechanism of action

FUNCTION OF SALIVA FUNCTION: LUBRICATION SALIVARY COMPONENT : Glycoprotein, mucoid PROBABLE MECHANISM :coating similar to gastric mucin FUNCTION: BUFFERING ACTION SALIVARY COMPONENT: Bicarbonates, phosphate MECHANISM : Antacid FUNCTION :PHYSICAL PROTECTION ,CLEANSING SALIVARY COMPONENT :Glycoproteins, mucoid, physical flow MECHANISM :clearance of bacteria and debris FUNCTION: TOOTH INTEGRITY ,MAINTAINANCE SALIVARY COMPONENT : Minerals ,glycoprotein pellicle MECHANISM :maturation ,remineralization mechanical protection SALIVARY COMPONENT :IGA MECHANISM : control of bacterial colonization FUNCTION: ANTIBACTERIAL ACTION SALIVARY COMPONENT :LYSOZYME MECHANISM OF ACTION : Break bacteria cells SALIVARY COMPONENT:L ACTOPEROXIDASE MECHANISM : oxidation of susceptible bacteria